Where to Buy Hybrid Power Systems in the Global Market?
When looking for Marine Hybrid Power System solutions, you need to carefully consider the skills, technology, and approval standards of the suppliers. There are many ways to get into the market, from specialized manufacturers like CM Energy to local wholesalers and business-to-business (B2B) sites. As the marine industry moves toward more environmentally friendly practices, ship owners are looking for combination power systems that use fuel, battery storage, and green energy sources. There are both obstacles and chances in this change for buying strategies that want to make sure they work well and meet environmental goals.
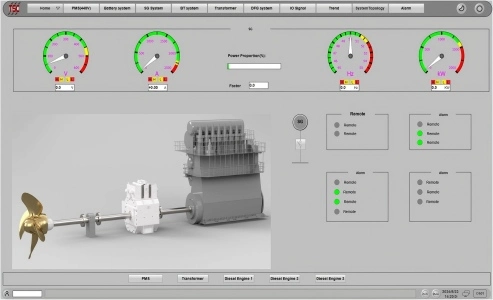
Understanding Marine Hybrid Power Systems and Their Global Applications
Core Components and Technologies
Modern Marine Hybrid Power System use more than one power source to maximize fuel efficiency and reduce pollution. Diesel engines, battery storage units, electric motors, and power control systems are often all part of these systems. Energy management is necessary to ensure that all the different power sources work together effectively.
Power circuits manage the flow of electricity between parts, making sure that switching between modes of operation is smooth. Smart grid technologies allow load sharing to happen automatically based on how the system is used. Fuel cells are becoming a more important addition to standard power sources, especially for backup systems.
Vessel Categories and Applications
Offshore wind turbine installation ships can be very helpful when they have hybrid engines that allow for exact positioning while the turbines are being installed. To run their dynamic tracking systems and do heavy work, these specialized ships need a lot of power.
Hybrid-electric cruise ships store energy in batteries so they can operate quietly in harbors and reduce pollution in areas that are important to the environment. Power optimization systems control how energy is split between safety systems, room loads, and transportation.
Port tugboats and harbor assistance vessels operate in emission-controlled zones where diesel generators alone cannot meet environmental standards. Electric motors provide instant torque for towing operations while reducing carbon footprint.
Research and survey vessels demand quiet operation for scientific equipment functionality. Hybrid propulsion systems enable autonomous operation modes essential for extended research missions.
Electric boats with no pollution are the way of the future for short-distance public travel. For power and other devices, these boats only use batteries for storing and green energy gathering.
Global Supply Chain Analysis for Marine Power Solutions
Market Dynamics and Regional Strengths
Asian makers control most of the production world because they have the most advanced technology and a long history of making ships. Major providers are based in places like China, South Korea, and Japan. These countries offer a wide range of services, from making parts to putting together whole systems.
European suppliers concentrate on high-end uses and specialized ships that need to meet strict energy saving standards. Nordic countries are especially good at developing technologies for ocean support vessels and environmentally friendly ways to ship goods.
North American suppliers put a lot of emphasis on coming up with new ideas for defense uses and self-driving boats. A lot of the time, these businesses are the first to use new technologies that are later used in commercial marine markets.
Demand Patterns Across Different Sectors
Most of the demand for Marine Hybrid Power System comes from commercial ships. To meet IMO pollution rules, more and more container ships and bulk carriers are using these systems.
As the offshore energy industry grows, there is a big need for specialized boats. When installing and maintaining wind farms, ships need to be able to handle a lot of power.
In naval and coast guard uses, speed and dependability are more important than cost. These clients often push technological progress by having strict business needs.
Technology that is at the leading edge and the ability to operate quietly are both necessities for luxury boat markets. The owners of superyachts usually include the most recent hybrid technology in their specifications, regardless of the financial repercussions.
Procurement Channels and Sourcing Strategies
Direct Manufacturer Relationships
| Channel Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Manufacturers | Lower costs, customization, technical support | Higher MOQs, longer lead times | Large projects, custom specifications |
| Local Distributors | Local support, faster delivery, lower MOQs | Higher prices, limited customization | Standard applications, urgent needs |
| B2B Platforms | Price comparison, supplier variety | Quality uncertainty, limited support | Price-sensitive purchases |
| Trading Companies | Market knowledge, consolidated shipping | Additional markup, less control | Multi-component projects |
Working directly with manufacturers like CM Energy provides access to engineering expertise and customization capabilities. These relationships enable collaborative development of solutions tailored to specific vessel requirements.
Regional Distribution Networks
For example, local dealers can help with installation, keep a collection of extra parts, and handle guarantee issues. These partners know the local rules and licensing standards that are necessary to follow them.
Comparing suppliers and finding the best prices is easier with B2B platforms, but you need to make sure that the technical skills and quality standards are met. Instead of whole systems, these bases work best for normal parts.
Trading Company Advantages
Trading businesses help with complicated projects that involve a lot of different sellers by gathering information about the market and coordinating buying. They often coordinate supplies and handle visa processes, which makes buying things from other countries easier.
Supplier Evaluation and Quality Assurance
Technical Qualification Criteria
When looking at possible providers, you need to look at their technical skills, production facilities, and quality control systems. Certifications from classification societies are a reliable way to check someone's expert knowledge.
Patent portfolios indicate innovation capabilities and technological leadership. Companies with extensive intellectual property demonstrate commitment to research and development.
Manufacturing capacity and production scalability affect project timelines and cost structures. Suppliers must demonstrate ability to handle project volumes within required delivery schedules.
Financial and Operational Stability
Supplier financial health impacts project risk and long-term support availability. Public companies provide transparent financial reporting, while private companies may require additional due diligence.
Geographic diversification of manufacturing facilities reduces supply chain risks. Multiple production locations provide flexibility during disruptions or capacity constraints.
Quality management system certifications ensure consistent product quality and process controls. ISO standards provide baseline requirements, while marine-specific certifications address industry requirements.
Performance Verification Methods
Reference installations provide practical evidence of supplier capabilities and product performance. Site visits enable direct assessment of operational systems and customer satisfaction.
Third-party testing and certification verify technical specifications and safety compliance. Independent validation reduces technical risks and supports financing arrangements.
Pilot projects allow evaluation of supplier capabilities on smaller scales before committing to major installations. These arrangements benefit both parties through reduced risk exposure.
Practical Procurement Considerations
Minimum Order Quantities and Commercial Terms
Most marine hybrid power system suppliers require substantial minimum orders due to customization requirements and engineering costs. Complete systems typically involve higher MOQs than individual components.
Payment terms vary significantly based on project size and supplier relationships. Standard terms often include advance payments for engineering work and progress payments during manufacturing.
Delivery schedules depend on customization requirements and supplier capacity. Standard configurations may ship within months, while custom systems require longer lead times.
Quality Control and Inspection Protocols
Factory acceptance testing verifies system performance before shipment. These procedures should include all operational modes and integration testing with vessel systems.
Third-party inspection services provide independent verification of manufacturing quality and specification compliance. These services become essential for large projects or new suppliers.
Documentation requirements include technical manuals, spare parts lists, and maintenance procedures. Complete documentation packages support operational training and long-term maintenance.
Common Procurement Pitfalls
Inadequate specification development leads to performance gaps and cost overruns. Clear technical requirements prevent misunderstandings and ensure competitive bidding.
Insufficient supplier qualification creates technical and commercial risks. Thorough evaluation processes identify potential issues before contract execution.
Poor integration planning causes delays and additional costs during installation. Early involvement of integration specialists prevents compatibility issues.
Installation and Commissioning Support
Technical Support Services
On-site installation ensures proper integration, with technicians identifying issues early. System commissioning includes testing of components and safety systems. Training programs prepare crews for operation and basic maintenance, reducing risks and extending system life.
Long-term Service Considerations
Spare parts availability impacts operations and maintenance costs, requiring suppliers to offer strong inventory management and global distribution. Remote monitoring aids predictive maintenance, reducing disruptions. Software updates and tech upgrades extend system life, ensuring compliance, with clear paths for upgrades and backward compatibility.
Conclusion
Sourcing marine hybrid power systems requires balancing technical requirements, commercial considerations, and supplier capabilities. The global market offers diverse options from specialized manufacturers to regional distributors, each with distinct advantages. Successful procurement depends on thorough supplier evaluation, clear specifications, and comprehensive quality assurance processes. As the maritime industry continues its transition toward sustainable operations, choosing the right supplier partnership becomes increasingly critical for long-term success. Understanding these procurement fundamentals enables informed decisions that optimize vessel performance while minimizing risks.
FAQ
1. What certifications should marine hybrid power systems have?
Marine hybrid power systems require classification society certifications from organizations like DNV, ABS, Lloyd's Register, or Bureau Veritas. These certifications verify compliance with international maritime safety standards and environmental regulations. Additional certifications may include IMO guidelines and flag state requirements.
2. How long does it take to deliver a complete marine hybrid power system?
Delivery times vary significantly based on customization requirements and supplier capacity. Standard configurations typically require several months, while fully customized systems may take longer. Complex installations for specialized vessels often require extended lead times due to engineering and integration requirements.
3. What factors influence marine hybrid power system pricing?
Pricing depends on power capacity, battery storage requirements, customization level, and certification needs. Additional factors include installation complexity, training requirements, and service agreements. Volume purchases and long-term partnerships often provide cost advantages.
4. How do I verify supplier technical capabilities?
Verify supplier capabilities through reference installations, classification society certifications, and patent portfolios. Site visits and pilot projects provide practical evaluation opportunities. Third-party technical audits offer independent assessment of manufacturing capabilities and quality systems.
5. What maintenance support should suppliers provide?
Comprehensive maintenance support includes spare parts availability, technical documentation, training programs, and remote monitoring capabilities. Suppliers should offer global service networks and 24/7 technical support for critical applications. Clear service level agreements define response times and performance guarantees.
Partner with CM Energy for Advanced Marine Hybrid Power System Solutions
CM Energy stands as a leading marine hybrid power system manufacturer with decades of maritime engineering expertise. Our comprehensive solutions integrate generator control systems, power management systems, energy storage technologies, and shaft generator systems for diverse vessel applications. With numerous authorized patents and extensive global offshore equipment coverage, we deliver proven performance for offshore wind installation vessels, hybrid cruise ships, and specialized marine craft. Contact our team at info.cn@cm-energy.com to discuss your project requirements and discover how our integrated packaging solutions can optimize your vessel's performance while reducing operational costs.
References
1. International Maritime Organization. "Guidelines for the Development of a Ship Energy Efficiency Management Plan." Maritime Safety Committee Resolution MSC.393(95), 2015.
2. Maritime and Coastguard Agency. "Marine Guidance Note 543: Hybrid and Electric Propulsion Systems for Commercial Vessels." United Kingdom Maritime Authority, 2023.
3. American Bureau of Shipping. "Guide for Battery Power on Ships." ABS Technical Standards and Guidelines, 2022.
4. DNV GL Maritime. "Alternative Fuels for Shipping: Technology Brief - Hybrid Power Systems." Norwegian Maritime Classification Society, 2023.
5. Society of Naval Architects and Marine Engineers. "Marine Electrical and Hybrid Propulsion Systems: Design and Integration Practices." SNAME Technical Publication, 2022.
6. International Association of Classification Societies. "Requirements for Electric Power Systems on Ships with Hybrid Propulsion." IACS Common Structural Rules, 2023.
