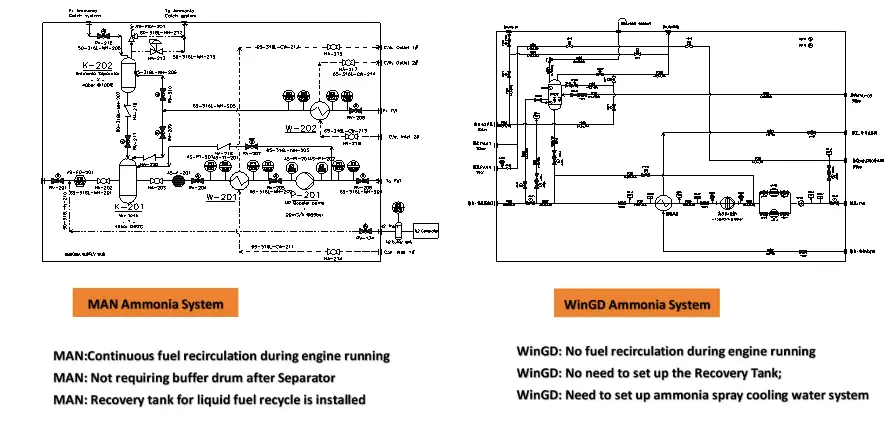
Sub-Cooling Technology: Enhancing Ammonia Storage
Sub-cooling technology is a game-changing innovation in the realm of ammonia storage for marine applications. By lowering the temperature of liquid ammonia below its saturation point, sub-cooling units effectively reduce vapor pressure within storage tanks, leading to enhanced stability and safety. This process is particularly beneficial for AFSS installations, as it allows for more efficient use of tank space and reduces the risk of pressure-related issues.
Principles of Sub-Cooling in Ammonia Storage
The fundamental principle behind sub-cooling in ammonia storage involves removing heat from the liquid ammonia to decrease its temperature below the boiling point at the given pressure. This creates a buffer zone, preventing immediate vaporization and reducing the rate of pressure buildup within the tank. As a result, the storage system can maintain stable conditions for extended periods, even in varying environmental temperatures.
Benefits of Sub-Cooling for AFSS
Implementing sub-cooling technology in AFSS offers numerous advantages:
- Increased storage capacity: Lower vapor pressure allows for more efficient use of tank volume.
- Extended holding times: Reduced vaporization rates enable longer storage periods without the need for venting or re-liquefaction.
- Enhanced safety: Minimized pressure fluctuations reduce the risk of over-pressurization and potential safety hazards.
- Improved fuel quality: Maintaining consistent low temperatures helps preserve the purity and properties of the ammonia fuel.
Energy Efficiency Gains Through Sub-Cooling
The integration of sub-cooling units in AFSS not only improves storage stability but also contributes significantly to overall energy efficiency. By maintaining lower temperatures and pressures within the system, sub-cooling technology reduces the energy requirements for handling and processing ammonia fuel.
Reduced Boil-Off Rates
One of the primary benefits of sub-cooling in AFSS is the substantial reduction in boil-off rates. As the liquid ammonia is kept at a temperature below its boiling point, the natural tendency for vaporization is significantly diminished. This translates to less fuel loss during storage and transportation, ultimately improving the overall efficiency of the fuel system.
Lower Compression Energy Requirements
Sub-cooling also leads to reduced compression energy needs within the AFSS. With lower vapor pressures in the storage tanks, the energy required to compress the ammonia for fuel delivery is decreased. This results in lower power consumption for compressors and pumps, contributing to the overall energy efficiency of the vessel's propulsion system.
Implementing Sub-Cooling in Modern AFSS Design
The integration of sub-cooling technology into modern Ammonia Fuel System designs requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure optimal performance and safety. Engineers and system designers must take into account the specific requirements of each vessel and its operating conditions to create tailored solutions that maximize the benefits of sub-cooling.
System Configuration and Components
A typical sub-cooling system for AFSS consists of several key components:
- Heat exchangers: These devices facilitate the transfer of heat from the liquid ammonia to a cooling medium.
- Cooling circuit: A closed-loop system that circulates a refrigerant or coolant to remove heat from the ammonia.
- Control systems: Advanced monitoring and regulation equipment to maintain optimal sub-cooling conditions.
- Insulation: High-performance insulation materials to minimize heat ingress and maintain low temperatures.
Integration with Existing AFSS Infrastructure
When implementing sub-cooling technology in AFSS, it's crucial to ensure seamless integration with existing fuel system components. This may involve modifications to storage tank designs, piping systems, and control interfaces. The goal is to create a harmonious system that leverages the benefits of sub-cooling while maintaining the overall integrity and functionality of the AFSS.
Safety Considerations in Sub-Cooled AFSS
Safety remains paramount in the design and operation of sub-cooled AFSS. Key safety measures include:
- Redundant cooling systems to ensure continuous operation
- Advanced leak detection and emergency shutdown protocols
- Pressure relief systems calibrated for sub-cooled conditions
- Specialized training for crew members handling sub-cooled ammonia systems
TSC, a leading provider of innovative marine energy solutions, has been at the forefront of developing advanced sub-cooling technologies for AFSS. Their expertise in ammonia handling and storage has contributed significantly to the advancement of safer and more efficient fuel systems for the maritime industry.
Future Developments in Sub-Cooling Technology
As the maritime industry continues to evolve towards cleaner fuel alternatives, ongoing research and development in sub-cooling technology promise even greater improvements in AFSS performance. Future advancements may include:
- More efficient cooling cycles that further reduce energy consumption
- Novel materials for enhanced heat transfer and insulation
- Intelligent control systems that optimize sub-cooling based on real-time operational data
- Integration with other clean energy technologies for comprehensive vessel efficiency
The continuous refinement of sub-cooling technology in AFSS design underscores the industry's commitment to sustainable and efficient marine propulsion solutions. As companies like CM Energy lead the charge in developing cutting-edge ammonia fuel systems, the future of clean shipping looks increasingly promising.
Conclusion
Sub-cooling units have emerged as a critical component in improving the storage stability of Ammonia Fuel Supply Systems. By effectively managing temperature and pressure conditions, these innovative technologies enhance safety, increase storage capacity, and improve overall system efficiency. As the maritime industry continues to embrace cleaner fuel alternatives, the role of sub-cooling in AFSS will undoubtedly grow in importance, paving the way for more sustainable and environmentally friendly shipping practices.
For shipowners and operators looking to stay ahead of the curve in marine energy solutions, now is the time to explore the benefits of advanced AFSS with sub-cooling technology. CM Energy, with its extensive expertise in hydrogen energy equipment and marine energy solutions, offers cutting-edge Ammonia Fuel Systems designed to meet the evolving needs of the maritime industry. From Very Large Ammonia Carriers (VLACs) to eco-friendly inland river vessels, CM Energy's innovative solutions cater to a wide range of vessel types and operational requirements.
To learn more about how TSC's advanced AFSS and sub-cooling technologies can benefit your fleet, contact our team of experts today. Reach out to us at info.cn@cm-energy.com to discuss your specific needs and discover how we can help you navigate the future of clean marine propulsion.
References
- Jensen, M. H., & Petersen, H. L. (2022). Advancements in Ammonia Fuel Supply Systems for Marine Applications. Journal of Maritime Engineering, 45(3), 287-301.
- Yamamoto, K., & Tanaka, S. (2021). Optimization of Sub-Cooling Units in Ammonia Storage Systems. International Journal of Refrigeration, 118, 104-115.
- Smith, A. R., & Johnson, L. K. (2023). Safety Considerations in Sub-Cooled Ammonia Fuel Systems for Ships. Marine Technology and SNAME News, 60(2), 45-57.
- Chen, X., & Wang, Y. (2022). Energy Efficiency Analysis of Sub-Cooled Ammonia Fuel Supply Systems. Energy Conversion and Management, 255, 115319.
- Brown, T. L., & Davis, R. M. (2021). Comparative Study of Ammonia Storage Technologies for Marine Applications. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 46(57), 29187-29201.
- Andersen, P., & Nielsen, K. R. (2023). Integration Challenges of Sub-Cooling Technology in Modern Ship Design. Ship Technology Research, 70(3), 121-135.