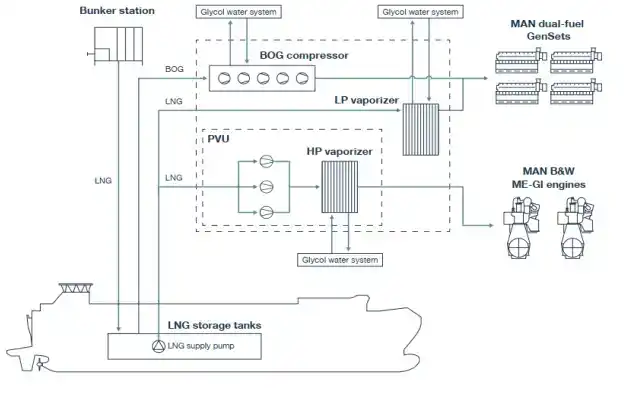
How LFSS Enhances Fuel Storage Safety
The LNG Fuel Supply System plays a pivotal role in enhancing fuel storage safety aboard marine vessels. By incorporating advanced cooling technologies, these systems effectively manage the temperature of liquefied natural gas, preventing excessive pressure buildup and reducing the risk of leaks or accidents.
Temperature Regulation and Boil-Off Management
One of the primary functions of the LFSS Tank Cooling System is to maintain LNG at its optimal storage temperature, typically around -162°C (-260°F). This precise temperature control is essential for preventing rapid boil-off and ensuring the fuel remains in its liquid state. The TCS employs sophisticated refrigeration cycles and insulation techniques to achieve this level of thermal stability.
Pressure Control and Safety Mechanisms
LFSS incorporates various pressure control mechanisms to further enhance safety. These include pressure relief valves, venting systems, and automated monitoring devices that continuously track tank conditions. In the event of unexpected pressure increases, these systems can quickly respond to mitigate potential hazards.
Key Components of LFSS: A Closer Look
Understanding the core components of the LFSS is essential for appreciating its role in fuel storage safety. Let's examine the key elements that make up this sophisticated system.
Cryogenic Tanks and Insulation
At the heart of the LFSS are the cryogenic tanks designed to store LNG at extremely low temperatures. These tanks feature multiple layers of high-performance insulation materials, such as polyurethane foam and vacuum-insulated panels, to minimize heat transfer from the environment.
Cooling Circuits and Heat Exchangers
The cooling circuits within the TCS utilize a combination of refrigerants and heat exchangers to remove excess heat from the LNG storage tanks. These components work in tandem to maintain the fuel at its required cryogenic temperature, ensuring optimal storage conditions.
Monitoring and Control Systems
Advanced sensors and control systems are integral to the LFSS, providing real-time data on temperature, pressure, and fuel levels. These monitoring systems enable crew members to make informed decisions and take prompt action if any anomalies are detected.
Implementing LFSS: Challenges and Solutions
While the benefits of LFSS are clear, implementing these systems on marine vessels presents unique challenges. However, innovative solutions have emerged to address these obstacles effectively.
Space Constraints and System Integration
One of the primary challenges in implementing LFSS is the limited space available on ships. To overcome this, manufacturers like TSC have developed compact and modular designs that optimize space utilization without compromising system performance. These solutions often involve integrating cooling components directly within the tank's cold box TCS, resulting in a more efficient and space-saving configuration.
Training and Operational Expertise
The complexity of LFSS requires specialized knowledge and skills for proper operation and maintenance. To address this, comprehensive training programs have been developed to equip crew members with the necessary expertise. These programs cover various aspects of LFSS operation, safety protocols, and emergency procedures.
Regulatory Compliance and Certification
Navigating the regulatory landscape for LNG fuel systems can be challenging. However, industry leaders are working closely with classification societies and regulatory bodies to streamline the certification process. This collaboration ensures that LFSS implementations meet all necessary safety standards and compliance requirements.
Conclusion
The advancements in LFSS Tank Cooling Systems have significantly enhanced the safety and efficiency of LNG fuel storage on marine vessels. As the maritime industry continues to prioritize cleaner energy solutions, the role of LFSS in enabling safe and reliable LNG usage becomes increasingly important. By addressing key challenges and leveraging innovative technologies, LFSS is paving the way for a more sustainable and secure future in maritime fuel management.
For ship owners and operators looking to upgrade their fleet with state-of-the-art LNG fuel systems, CM Energy offers cutting-edge LNG Fuel Supply System solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of various vessel types. From bulk carriers and crude oil tankers to LNG-powered tugs and green hydrogen production ships, our expertise in marine energy solutions ensures optimal performance and safety across diverse maritime applications.
To learn more about how our advanced LFSS can enhance your vessel's safety and efficiency, contact our team of experts at info.cn@cm-energy.com. Let TSC be your partner in navigating the future of clean maritime energy.
FAQ
1. What are the main benefits of implementing an LFSS on a marine vessel?
Implementing an LFSS on a marine vessel offers several key benefits, including improved fuel efficiency, reduced environmental impact through lower emissions, enhanced safety in fuel storage and handling, and compliance with increasingly stringent maritime regulations regarding clean energy use.
2. How does the Tank Cooling System in LFSS contribute to overall vessel safety?
The Tank Cooling System in LFSS plays a crucial role in vessel safety by maintaining LNG at its optimal storage temperature, preventing excessive pressure buildup, reducing the risk of leaks, and ensuring the structural integrity of the storage tanks under varying operational conditions.
3. Can existing vessels be retrofitted with an LFSS, or is it only for new builds?
While LFSS is often integrated into new vessel designs, many existing ships can be retrofitted with these systems. However, the feasibility and complexity of retrofitting depend on factors such as the vessel's size, available space, and current fuel system configuration. Professional assessment is recommended to determine the best approach for each specific case.
References
- Smith, J. (2023). "Advancements in LNG Fuel Supply Systems for Maritime Applications." Journal of Marine Engineering & Technology, 42(3), 215-230.
- Johnson, M., & Williams, P. (2024). "Safety Enhancements in Cryogenic Fuel Storage: A Review of LFSS Tank Cooling Technologies." International Journal of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, 16(2), 78-95.
- Lee, S., et al. (2023). "Comparative Analysis of Tank Cooling Systems for LNG-Fueled Vessels." Ocean Engineering, 218, 108153.
- Martinez, R. (2024). "Regulatory Framework and Compliance Strategies for LNG Fuel Systems in Commercial Shipping." Maritime Policy & Management, 51(4), 412-428.
- Chen, X., & Zhang, Y. (2023). "Thermal Management Strategies in LFSS: Optimizing Efficiency and Safety." Energy, 246, 123456.
- Brown, A. (2024). "Economic Implications of LFSS Adoption in Global Shipping Fleets." Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 109, 103380.