Ammonia Fuel Handling System
Overview of the Ammonia Fuel Handling System
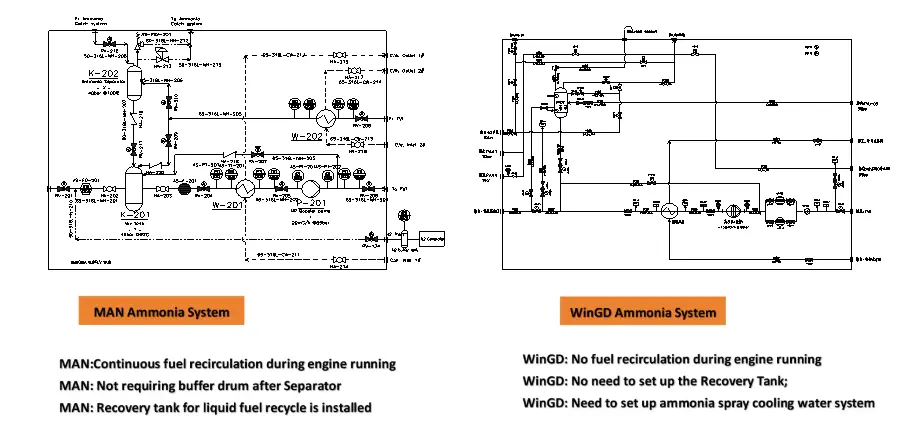
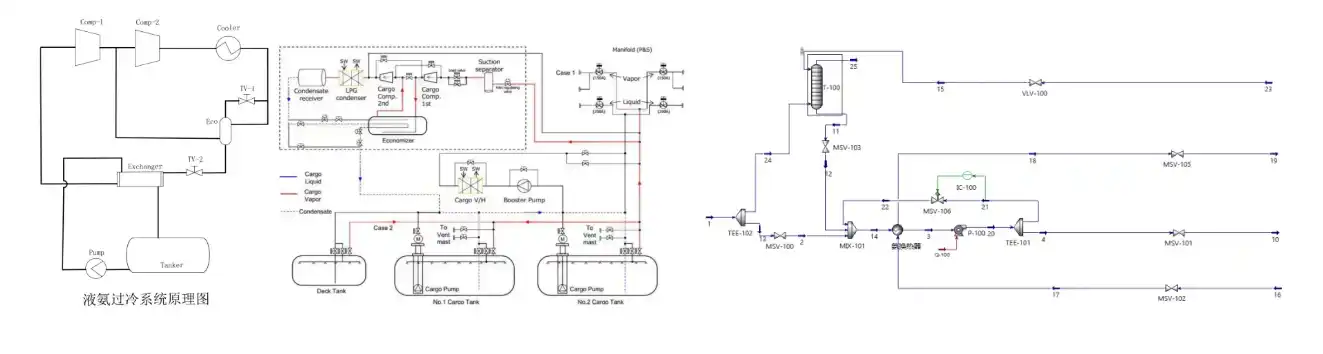
The Ammonia Fuel Handling System is made up of several key components, including the filling and storage system, the Ammonia Fuel Supply System (AFSS), the Fuel Value Unit (FVU), the venting system, the Ammonia Release Management System (ARMS), the ventilation system, the inert gas system, the engine’s internal ammonia fuel system, and the safety system. It is crucial to recognize the significant differences between the systems used by MAN and WinGD.
Why Choose Us?
1. Unmatched Industry Expertise – With extensive experience in the design and construction of dual-fuel vessels, liquefied gas carriers, chemical tankers, and their associated systems, we have established ourselves as an industry leader.
2. Comprehensive Service Portfolio – Our services encompass Methanol Fuel Supply Systems (MFSS), LNG Fuel Supply Systems (FGSS), Ammonia Fuel Supply Systems (AFSS), and LPG Cargo Handling Systems (CHS), all available under one roof.
3. Proven Excellence in Delivery – We have earned a strong reputation for reliability and quality, backed by the successful installation of 19 clean fuel supply and cargo handling systems.
4. Pioneering AFSS Development – Through our extensive knowledge of ammonia carrier construction and LPG retrofit projects, we independently develop ammonia fuel supply systems and actively contribute to zero-carbon research.
5. Comprehensive Lifecycle Support – From the design phase through manufacturing and final installation, we offer end-to-end support, including the construction of multiple units and comprehensive post-sales service.
Product Specifications

Product Features
1. Safety and Efficiency Combined – The Ammonia Fuel Handling System is designed to ensure safe and efficient ammonia bunkering and storage, meeting low-flashpoint fuel standards and IMO regulations while addressing the specific ammonia fuel requirements of the marine sector.
2. Advanced Flow and Safety Management – The system is equipped with precise flow regulation and integrates advanced safety features, such as emergency shutdowns, leak detection, and compatibility with inert gas systems to protect operations.
3. Environmental Stewardship – With a focus on reducing environmental impact, the system includes vapor management technologies like thermal oxidation and re-liquefaction to safely handle ammonia, particularly in low-pressure storage environments.
4. Ventilation and Hazard Mitigation – It provides robust ventilation for both above-deck and enclosed spaces, while incorporating inert gas technologies to minimize explosion risks in potentially hazardous areas.
5. Pressure Regulation Capabilities – By utilizing sub-cooling or re-liquefaction units alongside thermal oxidation systems, the system effectively controls ammonia vapor pressure in low-pressure tanks, thereby enhancing operational safety.
Installation Process
1. Examine Vessel Design – Begin by thoroughly reviewing the vessel’s design and system interface requirements, ensuring that all technical uncertainties are resolved before proceeding.
2. Pre-Installation Preparations – Before installation, verify that all necessary tools, equipment, and safety protocols are in place and ready for deployment.
3. Component Transportation – Transport the pre-assembled fuel supply system module to the installation location using appropriate lifting devices, ensuring accurate positioning at the designated mounting point.
4. Securing the Module – Securely fasten the module base to the vessel’s structure, ensuring proper alignment and stability according to the design parameters.
5. System Connections – Connect the fuel transfer lines, auxiliary piping, and control systems, ensuring the functionality of all electrical and sealing components.
6. Commissioning the System – Perform individual and integrated debugging procedures to verify the performance of all subsystems, including bunkering, fuel delivery, and safety monitoring functions.
For more product information about Ammonia Fuel Handling System, please leave a message below.
